Understanding Fats: An Overview
Fats are a critical component of the human diet, performing essential functions in the body. They serve as a major energy source and help absorb vital nutrients. There are several types, but they primarily fall into two categories: saturated and unsaturated fats. Saturated fats, usually solid at room temperature, are found in animal products like butter and cheese. Unsaturated fats, typically liquid, come mostly from plant sources such as olive oil and fish. It’s important to distinguish these sources because they impact health differently. Understanding these distinctions is key to making informed dietary choices.
What Are Healthy Fats?
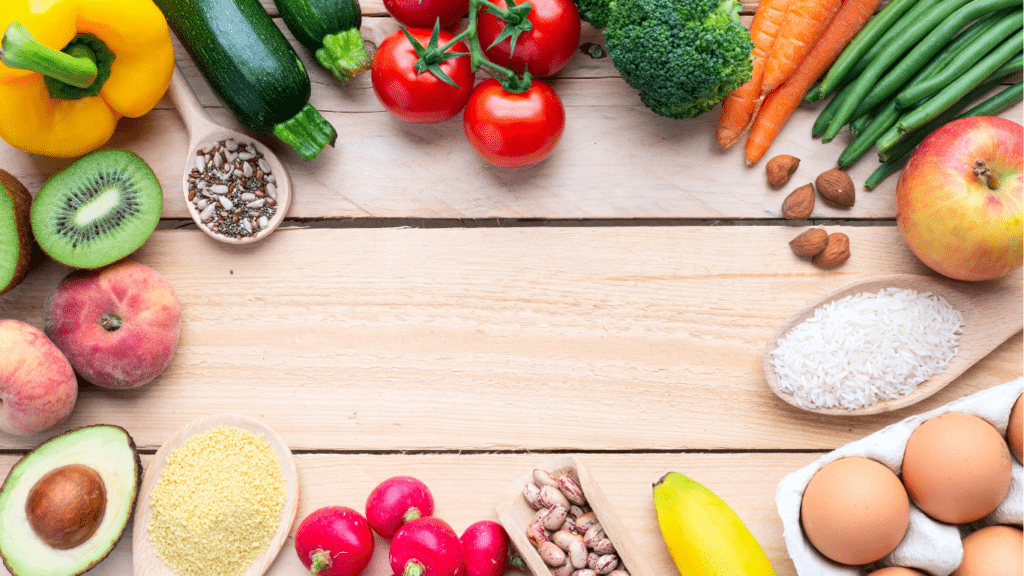

Healthy fats, essential for overall well-being, enhance body functions and prevent chronic diseases. Incorporating these fats into your diet promotes a healthier lifestyle.
Types of Healthy Fats
- Monounsaturated Fats: Commonly found in avocados and olives, these fats support heart health by improving cholesterol levels.
- Polyunsaturated Fats: Present in fatty fish like salmon and seeds like flaxseed, these fats are vital for brain function and reduce inflammation.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in walnuts and chia seeds, omega-3s play a crucial role in reducing heart disease risk.
- Omega-6 Fatty Acids: Although necessary, omega-6s should be balanced with omega-3s for optimal health; sources include sunflower oil and nuts.
Benefits of Healthy Fats
Healthy fats offer numerous health advantages. They help lower bad cholesterol (LDL) while increasing good cholesterol (HDL), reducing heart disease risk. By supporting brain health, these fats improve memory and cognitive functions. They also aid in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins like A, D, E, and K, enhancing nutritional intake. Including these fats in your diet supports healthy skin and hormone production, contributing to overall vitality.
What Are Unhealthy Fats?
Unhealthy fats often contribute to a range of health issues. Recognizing them is essential for making beneficial dietary decisions.
Types of Unhealthy Fats
Unhealthy fats primarily include trans fats and certain saturated fats. Trans fats, often artificial, are found in partially hydrogenated oils. These oils are common in processed foods like snacks and baked goods. Consuming trans fats raises LDL cholesterol levels, increasing heart disease risk. Some saturated fats, primarily from animal sources like fatty cuts of meat and dairy products, also fall under unhealthy fats. These fats can, in excess, contribute to high cholesterol.
Risks Associated with Unhealthy Fats
Consuming unhealthy fats can lead to serious health concerns. High intake of trans fats increases the risk of heart disease and stroke by altering cholesterol levels. Saturated fats, when consumed in excess, can similarly raise LDL cholesterol, heightening heart disease risk. Additionally, diets high in these fats can contribute to weight gain and obesity-related conditions such as type 2 diabetes. Understanding these risks helps in making informed choices to minimize their intake.
How to Identify Healthy vs. Unhealthy Fats
Distinguishing between healthy and unhealthy fats is crucial for better dietary choices. I focus on reading food labels and identifying common sources to help determine fat quality.
Reading Food Labels
Food labels serve as a vital tool in identifying fat types. I pay attention to the nutrition facts panel and the ingredients list. The total fat section provides information on saturated, trans, monounsaturated, and polyunsaturated fats. Avoid trans fats by looking for “partially hydrogenated oils” in ingredients. Additionally, I note the ratio of unsaturated to saturated fats, aiming to increase unsaturated fats.
Common Sources of Each
Identifying common fat sources helps make informed choices.
- Healthy fats: I include avocados, nuts (almonds, walnuts), seeds (flaxseeds, chia seeds), fatty fish (salmon, mackerel), and plant oils (extra-virgin olive oil, canola oil).
- Unhealthy fats: These include processed foods (cakes, cookies), fried items, fast foods, and certain animal products (fatty cuts of meat, full-fat dairy). Trans fats often hide in snack foods and margarine.
Through mindful label reading and source identification, I can prioritize healthy fats and limit unhealthy ones.
Incorporating Healthy Fats into Your Diet
Introducing healthy fats into your diet can significantly boost overall health. They offer essential benefits and can be seamlessly integrated into daily meals with a few mindful choices.
Meal Planning Tips
Prioritize diversity, incorporating various sources of healthy fats to ensure a well-rounded intake. Include avocados in salads or as spreads, and opt for olive oil in place of butter for cooking. Factor in snack-rich options like nuts and seeds, which can be carried easily. Aiming to balance meals with protein, healthy fats, and complex carbs enhances satiety and energy. Limit portions of high-calorie items, even if they contain healthy fats, to maintain a balanced calorie intake.
Healthy Fat-Rich Recipes
Embrace recipes featuring ingredients rich in healthy fats. Prepare a Mediterranean salad with olives, avocados, and a drizzle of olive oil for a refreshing side. Try baking salmon with a crust of crushed walnuts, achieving a crispy texture and robust taste. For breakfast, enjoy chia seed pudding mixed with almond milk and topped with fruit, offering a nutritious start. Experiment with different spice-infused nut mixes for healthy snacking. Integrating these recipes ensures sustained inclusion of beneficial fats into your daily meals.


 Senior Sports Writer
Alfred Alder is the senior sports writer at Sprint Scoop News, bringing his extensive knowledge of fitness, training, and sports business to the forefront. With a career spanning more than a decade, Alfred specializes in delivering high-quality, engaging content that covers everything from sponsorship trends to the latest in health and nutrition for athletes. His deep understanding of the sports industry allows him to provide readers with comprehensive insights that make complex topics accessible and exciting.
Senior Sports Writer
Alfred Alder is the senior sports writer at Sprint Scoop News, bringing his extensive knowledge of fitness, training, and sports business to the forefront. With a career spanning more than a decade, Alfred specializes in delivering high-quality, engaging content that covers everything from sponsorship trends to the latest in health and nutrition for athletes. His deep understanding of the sports industry allows him to provide readers with comprehensive insights that make complex topics accessible and exciting.